
ABOUT EQUIPMENT
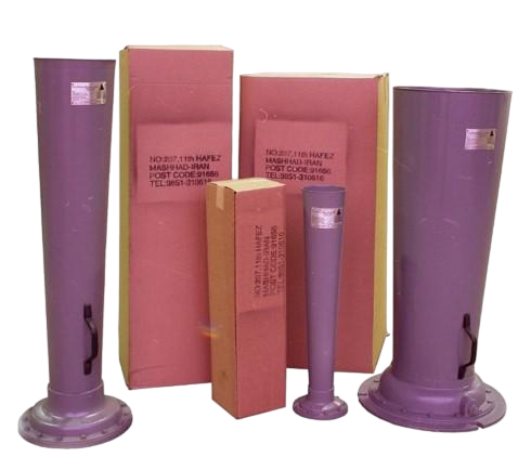
STRAINER
EQUIPMENT
A pipeline strainer is a device used to mechanically remove solids from a flowing fluid. This is accomplished by utilizing a perforated metal, mesh or wedge wire straining element.
The most common range of strainer particle retention is 1” to 40 microns (0.0016”). Strainers remove waste materials such as scale, rust, weld metal residues that get stuck in the pipeline and protect the piping equipment.
Strainers are employed in pipelines to protect downstream mechanical equipment such as condensers, heat exchangers, pumps, compressors, meters, spray nozzles, turbines, and steam traps from the detrimental effect of sediment, rust, pipe scale, or other extraneous debris.
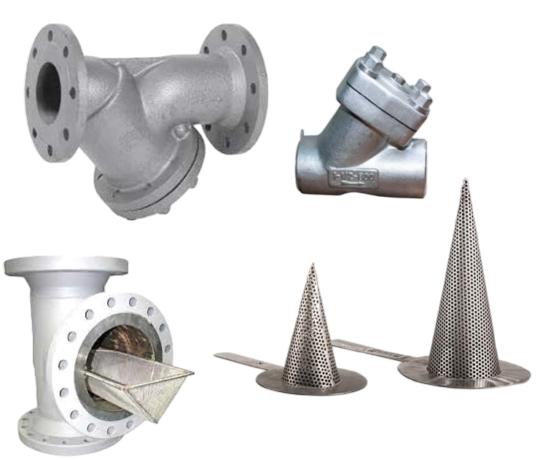
Types of strainers
“T” Type
“Y” Type
Cone Type
Basket Type
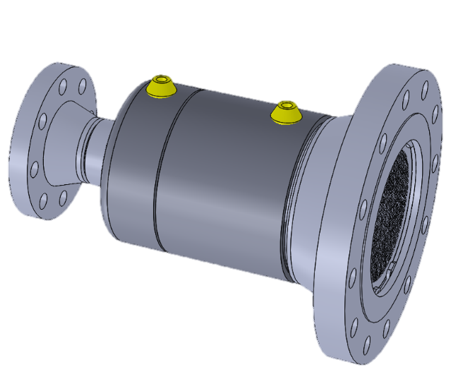
T-Type Strainer
The T-strainer is designed in the shape of the letter T and has two inlet and outlet valves. In this type of strainer, the filter is a flat plate inside the inlet valve and fluids pass through it. This type of strainer is suitable for small and medium applications due to its simple structure and high efficiency.
Benefits
- Suitable for filtering fluids with larger solid particles
- Can be installed horizontally
- Low maintenance cost
End Connection
FlangedButt-Welding Ends

Y-Type Strainer
Y-type strainer, the filter base is connected to the main pipe at a diagonal angle and the strainer is placed in the Y position (hence its name). This type is typically used in pressurized, steam, liquid, or gas lines, but can also be used in vacuum or suction situations. When it is necessary to separate a small number of impurity particles from the fluid, the Y type strainer is preferred.
Also, this type of strainer is more efficient in situations where frequent maintenance does not cause much interruption to the system. Y type strainer is mostly used in cases where the pressure is more than 6000 PSI.
The Y-type strainer is not designed to hold particles and debris for long periods of time. As a result, the Y type requires more regular cleaning than other strainer types.
Benefits
- It is easy to clean and does not disrupt the system.
- Y type strainer can be selected from various dimensions of mesh and spring hole.
- It can be installed horizontally or vertically.
End Connection
FlangedThreadedSocket Welded

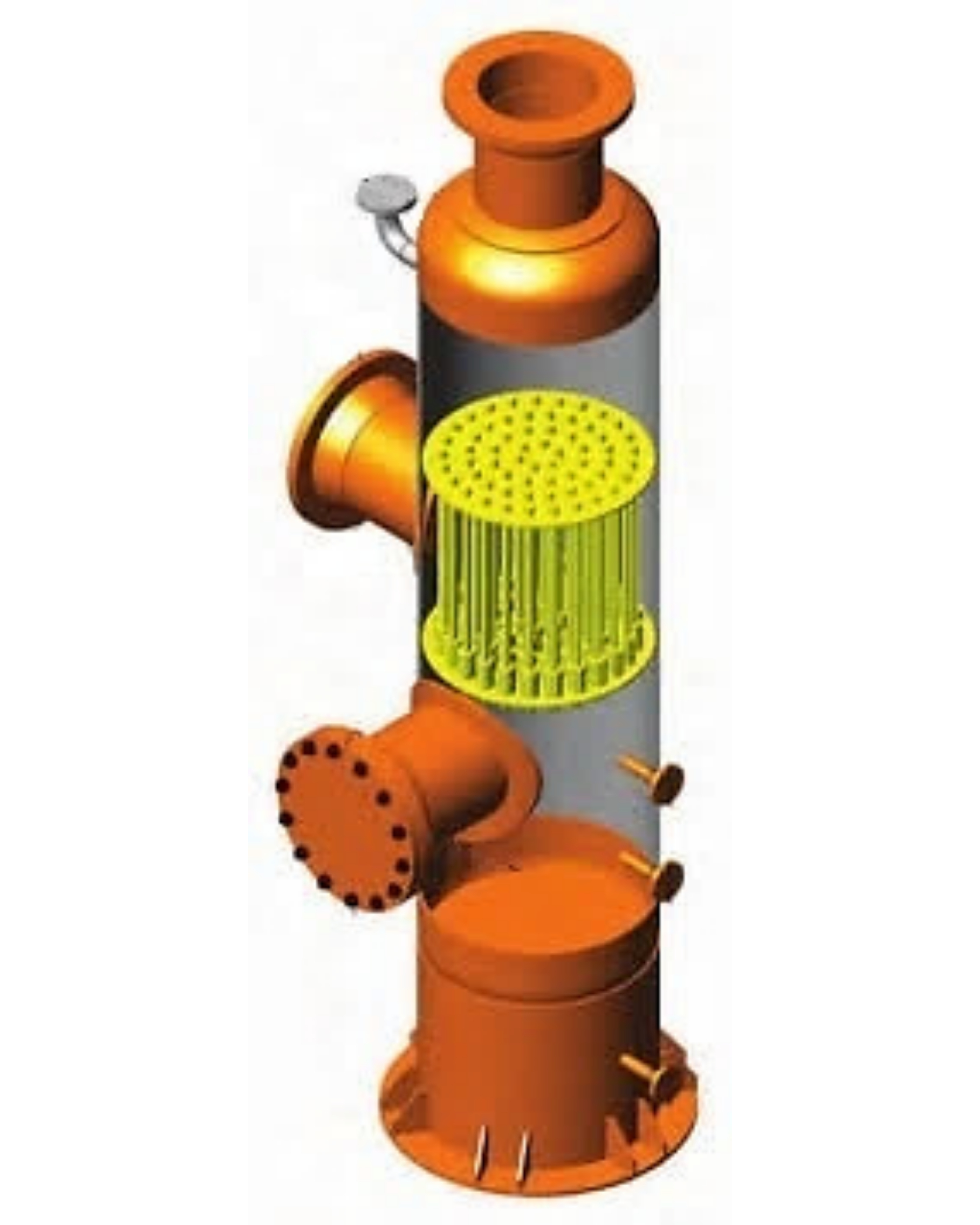
Cone Type Strainer
Conical strainers are installed in a metal body, between flanges, and work as a temporary or permanent filtering device.
Conical Strainers are very cost-effective solutions in many applications and suitable where the amount of material to be removed from the stream is relatively small and therefore there are long intervals between cleaning the screen. The strainer screen is cleaned manually by turning off the line and removing the strainer cap.
Conical strainers offer a large filtration area, letting you catch more debris. They’re often used for products that have been recently welded. During the welding process, it’s possible that slag or bits of debris may have formed inside the pipes. Conical strainers will catch these specks of metal before they travel down.
Where Used…?
Temporary strainer is installed to protect a flow meter, pump, control or relief valves or other pieces of equipment during startup.
During construction, materials may become trapped in the line. These materials could be welding slag, welding rod, pieces of wood, cigarettes, rocks, etc. Many pieces of equipment will become damaged if this debris enters it. After start up is completed, the startup strainer should be removed.
Connection Type
Flanged Strainer Will Be Installed Between Two R.F, ANSI B16.5 Flanges.
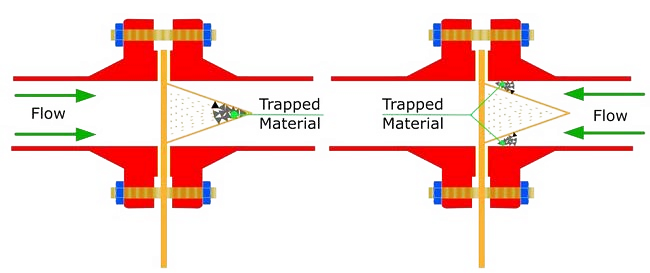
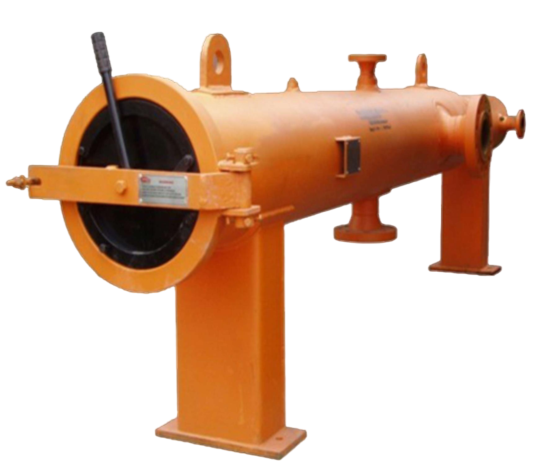
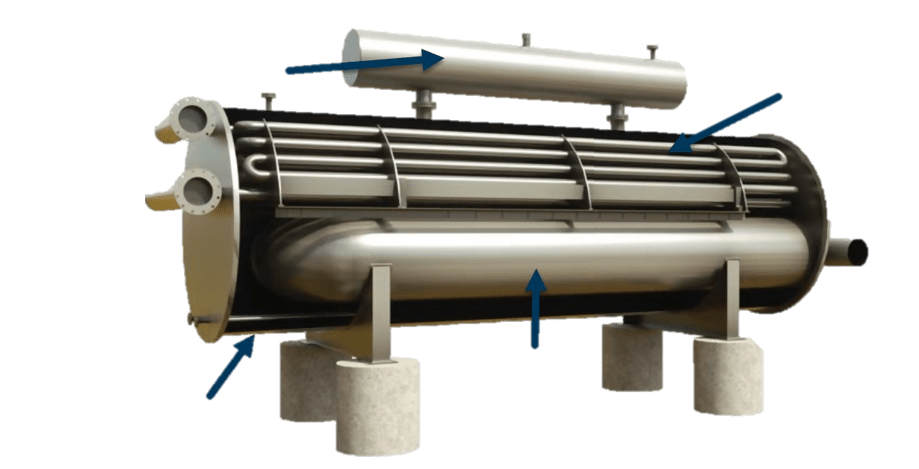
Basket Type Strainer
The basket type strainer has a vertical chamber that is typically larger than the Y strainer chamber. In all sizes, the pressure drop in the basket strainer is lower than in the Y strainer because of the larger free strainer space For this reason.
This strainer can hold more waste. Basket strainers can only be installed in parallel pipes, and for large and bulky basket strainers, the strainer base must be reinforced.
The cover on the basket strainer can be removed to allow operators easy access to the filter section when replacement or cleaning is required.
Application of Basket Strainer
the basket strainer is also used in larger diameter steam pipelines. The basket strainer is the opposite of the Y-type strainer. This type of strainer is suitable for fluids with large impurity particles that require frequent cleaning. Basket strainers are rarely used where pressures exceed 1500 PSI.
End Connection
FlangedWeldedThreaded

Filters VS Strainers
Filters can separate particles as small as one millimeter. Conversely, strainers can only remove larger particles from a liquid or gas.
Another difference is that strainers can be used multiple times, while filters can only be used once.
The amount of resistance is also different in filters and strainers. Strainers are a poor barrier to flow. In contrast, medium filters cause a large pressure drop in the system. Most strainers have minimal pressure drop.
The strainer is used to prevent the failure of piping equipment due to the entry of waste. If the filter is used to separate particles from the fluid.
Strainer Connection and Pipeline Alignment
Y or T type strainers are an ideal choice for vertical pipelines. On the other hand, basket strainers are a good choice for horizontal or moderately inclined pipelines. In this situation, the strainer is installed in the lowest possible position to allow easy washing of waste.
Standard Design of Strainers
Strainers are usually designed according to the following standards:
- ANSI B16.34
- PED 97/23/EC: Pressure Equipment Design
- BPVC: ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code, Sec. VIII Div.1
Perforations and Mesh Sizing
An extremely important consideration in the selection of a strainer is the size of the perforations mesh or wire opening used in the fabrication of the straining element.
A tendency exists to select smaller holes than those actually needed, leading to too frequent cleaning, excessive pressure drop, and screens constructed of thinner metal which will withstand less pressure differential. Generally, the maximum thickness of stainless steel perforated metal is one gage thickness less than the diameter of the punched holes. Carbon steel and brass can be obtained in approximately the same thickness as the punched hole diameter.
The following tables illustrate available perforated plate, mesh, and wedge wire and their respective straining capability. The main criteria for choosing hole and mesh size is the size and quantity of particles which can pass through downstream equipment without causing damage.
Hole spacing is the distance between the centers of two adjacent holes. For a given hole size, the greater the hole spacing, the lower the percentage open area of the perforated metal.
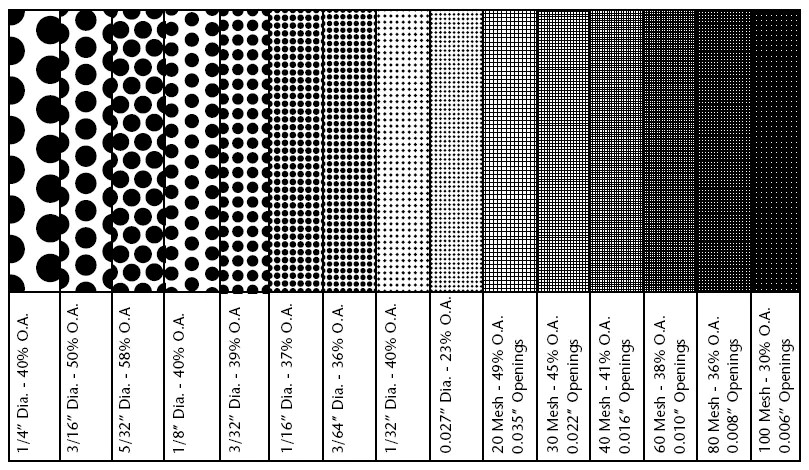
Strainer Screens
- Perforated Screen
- Mesh Screen
Perforated Screen
The diameter of springs ranges from 0.8 to 3.2 mm. Perforated plates are actually sheet shaped and can be shaped into tubes.
Mesh Screen
The mesh is actually a woven screen of thin wires. Filtering particles as small as 0.07 mm is possible with these meshes.














 Contact Us
Contact Us Engineering Group
Engineering Group
 Creative Strategy
Creative Strategy Download
Download